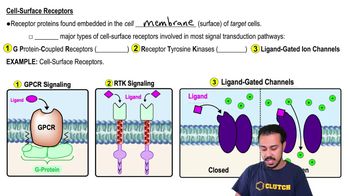
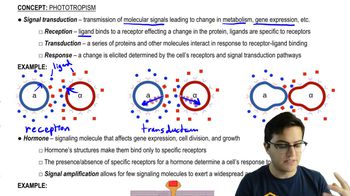
Which of the following is not an accurate statement?
a. Hormones are chemical messengers that travel to target cells through the circulatory system.
b. Hormones often regulate homeostasis through antagonistic functions.
c. Hormones of the same chemical class usually have the same function.
d. Hormones are often regulated through feedback loops.