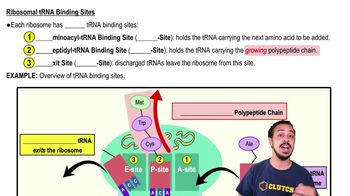
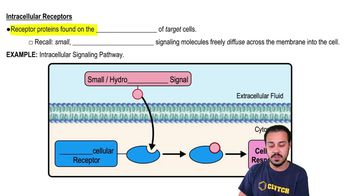
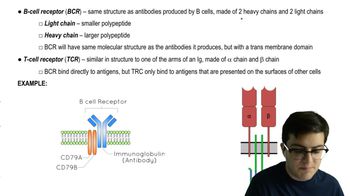
Which of the following statements is not true?
a. An antibody has more than one antigen-binding site.
b. A lymphocyte has receptors for multiple different antigens.
c. An antigen can have different epitopes.
d. A liver or muscle cell makes one class of MHC molecule.