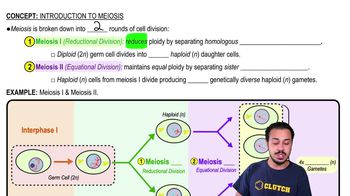
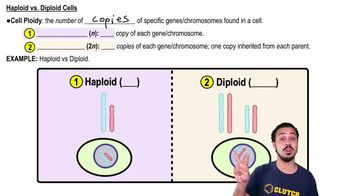
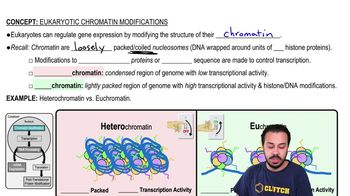
The production of gametes ________.
a. Begins at puberty in males and females.
b. Requires that the testes of males produce semen.
c. Results in the production of diploid cells from haploid cells.
d. Begins at puberty in females.
e. Produces sperm and eggs that carry half the number of chromosomes as nongametes.