Textbook Question
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by ________.
a. Heating cells
b. Binding to substrates and placing stress on their bonds
c. Changing the shape of the cell
d. Supplying energy to the substrate


 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
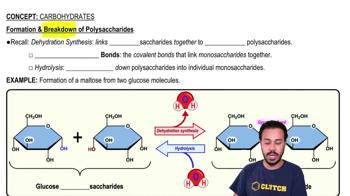

Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by ________.
a. Heating cells
b. Binding to substrates and placing stress on their bonds
c. Changing the shape of the cell
d. Supplying energy to the substrate
Which of the following is a false statement regarding enzymes?
a. Enzymes are proteins that speed up metabolic reactions.
b. Enzymes have specific substrates.
c. Enzymes supply ATP to their substrates.
d. An enzyme may be used many times.
What is meant by the term induced fit?