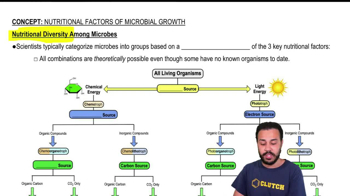
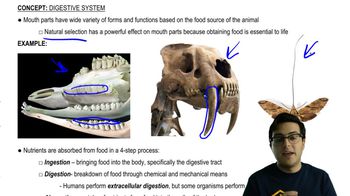
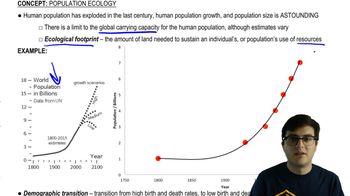
Comparisons of ribosomal RNA among many different modern species indicate that
a. There are two very divergent groups of prokaryotes
b. The Protista represents a conglomeration of very unrelated forms
c. Fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants
d. A and B are correct
e. A, B, and C are correct