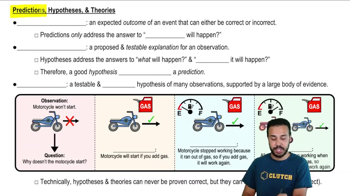
A scientific hypothesis is ________.
a. An opinion
b. A proposed explanation for an observation
c. A fact
d. Easily proved true
e. An idea proposed by a scientist

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
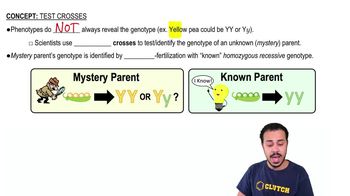

A scientific hypothesis is ________.
a. An opinion
b. A proposed explanation for an observation
c. A fact
d. Easily proved true
e. An idea proposed by a scientist
How is a scientific theory different from a scientific hypothesis?
a. It is based on weaker evidence
b. It has not been proved true
c. It is not falsifiable
d. It can explain a large number of observations
e. It must be proposed by a professional scientist
One hypothesis states that eating chicken noodle soup is an effective treatment for colds. Which of the following results does this hypothesis predict?
a. People who eat chicken noodle soup have shorter colds than do people who do not eat chicken noodle soup.
b. People who do not eat chicken noodle soup experience unusually long and severe colds.
c. Cold viruses cannot live in chicken noodle soup.
d. People who eat chicken noodle soup feel healthier than do people who do not eat chicken noodle soup.
e. Consuming chicken noodle soup causes people to sneeze.
Control subjects in an experiment _________.
a. Should be similar in most ways to the experimental subjects.
b. Should not know whether they are in the control or experimental group.
c. Should have essentially the same interactions with the researchers as the experimental subjects.
d. Help eliminate alternative hypotheses that could explain experimental results.
e. All of the above.
An experiment in which neither the participants in the experiment nor the technicians collecting the data know which individuals are in the experimental group and which ones are in the control group is known as _________.
a. Controlled
b. Biased
c. Double-blind
d. Falsifiable
e. Unpredictable
A relationship between two factors, for instance, between outside temperature and the number of people with active colds in a population, is known as a(n) ________.
a. Significant result
b. Correlation
c. Hypothesis
d. Alternative hypothesis
e. Experimental test